L.1- GEOGRAPHY AS A DISCIPLINE
1. There exist variations over the surface of the earth in its physical as well as cultural environment. This concept in Geography is suitably depicted by which of the following concepts ?
a. Spatial distribution
b. Areal differentiation
c. Areal variations
d. Differential relations
Ans. (b)
2. Which of the following concept is described by most of the scholars in the definition about geography ?
a. The Earth as the home of human being only
b. The earth as the abode of plants and animals
c. The earth as the abode of human beings
d. The earth and its cultural and physical features
Ans. ( c)
3. Choose the name of scholars who has given the following definition about geography’ ? “Geography is concerned with the description and explanation of the areal differentiation of the earth’s surface.”
a. Richard Hartshorne
b. Hettner
c. Vidal-de-la-blache
d. Ratzel
Ans. (a)
4. Geography is a discipline of synthesis which attempts --------------------------synthesis.
a. Temporal
b. Spatial
c. Collective
d. Physical
Ans. (b)
5. Which of the following is not matched correctly ?
a. Political Geography - Delimitation of constituencies
b. Historical Geography - Temporal changes of geographical phenomena
c. Soil Geography - Cultural elements
d. Geomorphology - Evolution of landforms
Ans. (c)
6. Process of Pedogenesis refers to the
a. Formation of landforms
b. Formation of mountains
c. Formation of tributaries
d. Formation of soils
Ans. (d)
7. All the sciences, whether natural or social, have one basic objective, of-----------------------. a. understanding the reality
b. World as a global village
c. Understanding the concepts of relations
d. Understanding the earth
Ans. (a)
8. Match the List I with List II and choose correct answer with the help of given codes. LIST I LIST II
I. Geography i scientific study of the habitats
II. History ii spatial characteristics and attributes III. Ecosystem iii infrastructure and services
IV. Economic geography iv Temporal synthesis
V. Hydrology v Realms of water
Options
I II III IV V
a. v i ii iii iv
b. i v ii iv iii
c. ii iv i iii v
d. I ii iii iv v
Ans. (c )
9. Which of the following approach of geography is given by Alexander Von Humboldt? a. Regional approach
b. Systematic approach
c. Traditional approach
d. Humanistic approach
Ans. (b)
10. Consider the following example carefully and identify the approach of geography reflected in it.
“A phenomenon is studied world over as a whole,and then the identification of typologies or spatial patterns is done”.
a. Welfare approach
b. Regional approach
c. Systematic approach
d. Environmental adaptation
Ans. ( c)
11. Consider the following statements and choose the correct answer from the given options I. Dualism is one of the main characteristics of geography which got introduced from the very beginning.
II. In the regional approach, the world is divided into regions at different hierarchical levels. III. The fertility of the soil is both naturally determined and culturally induced
Options :
a. Only I and II are correct
b. Only I and III are correct
c. Only II and III are correct
d. All are correct
Ans. (d)
12. Which of the following factors helped human beings to moved from the stage of necessity to a stage of freedom ?
a. Technology
b. Laws of nature
c. Literacy level
d. Availability of resources
Ans. (a)
13. Which of the following forms a correct group?
a. Economic geography, Geomorphology, Historical geography
b. Regional Analysis, Regional planning, Climatology
c. Geomorphology, Climatology, Hydrology, Soil geography
d. Social geography, Regional Development, Population and settlement, Hydrology
Ans. (c )
14. Earlier scholars were mainly focused on which of the following branch of geography? a. Human geography
b. Physical geography
c. Biogeography
d. Economic geography
Ans (b)
15. Which of the following is not a recent development in the field of geography? a. Explorations of new areas through voyages
b. Transformation of manual cartography into computer cartography
c. Development of GIS and GPS to increase knowledge
d. Availability of extensive information through internet
Ans (a)
16. Which of the following group of topics is included in the study of biosphere ? a. Drainage, landforms, relief
b. Oceans, lakes, rivers
c. Food chain, ecological balance, life forms including human beings
d. Temperature, pressure, climatic types
Ans. ( c)
17. Consider the following statements and choose the correct answer from the given options I. Accelerated pace of resourceutilisation with the help of modern technology has created ecological imbalance in the world.
II. A better understanding of physical environment is absolutely essential for sustainable Development.
III. The study of physical geography is emerging as a discipline of evaluating and managing human resources
Options :
a. Only I and II are correct
b. Only I and III are correct
c. Only II and III are correct
d. All are correct
Ans. (a)
18. Which of the following factor is essential for sustainable development?
a. To understand the nature of human being
b. To understand the nature of landforms
c. better understanding of human culture and their habits
d. a better understanding of physical environment
Ans. (d)
19. “Geography studies the differences of phenomena usually related in different parts of the earth’s Surface”.
Which of the following scholar had given above mentioned definition about the study area of geography ?
a. Hettner
b. Hartshorne
c. Ellen C. Semple
d. Wagener
Ans. (a)
20. Which of the following two factors are important for the density of forests and quality of Grasslands ?
a. Temperature and pressure
b. Temperature and evaporation
c. Pressure and humidity
d. Temperature and precipitation
Ans (d)
L-2 THE ORIGIN AND EVOLUTION OF THE EARTH
1. Which of the following is not matched correctly ?
SCIENTIST THEORIES
a. Immanuel Kant - Nebular hypothesis
b. Chamberlin & Moulton - Wandering star theory
c. James & Jean - Convectional current theory
d. Edwin Hubble - Big Bang Theory
Ans. (c)
2. Which of the following theory is also called as Expanding Universe Hypothesis ? a. Nebular hypothesis
b. Gaseous hypothesis
c. Binary star theory
d. Big Bang theory
Ans. (d)
3. Arrange the following stages of Big Bang in correct sequence and choose the correct answer from the given options.
I. Within 300,000 years from the Big Bang, temperature dropped to 4,500 K (Kelvin) and gave rise to atomic matter.
II. At the Big Bang the “tiny ball” exploded violently. This led to a huge expansion. III. all matter forming the universe existed in one place in the form of a “tiny ball” (singular atom) with an unimaginably small volume, infinite temperature and infinite density. IV. The expansion has slowed down. Within first three minutes from the Big Bang event,the first atom began to form.
Options :
a. III, II, IV, I
b. I, II, III, IV
c. I, III, IV, II
d. II, I, IV, III
Ans. (a)
4. A galaxy is a group of -----------------------------------.
a. Planets
b. Stars
c. Moon
d. Gases
Ans. (b)
5. A galaxy starts to form by accumulation of ----------------------- gas
a. Helium
b. Nitrogen
c. Hydrogen
d. Oxygen
Ans. (c)
6. Which of the following statement is not true regarding formation of the stars ? a. The stars are localised lumps of gas within a nebula.
b. the gas cloud starts getting condensed and the matter around the core develops into small rounded objects.
c. The small-rounded objects by the process of cohesion develop into planetesimals d. the small number of small planetesimals got separated to form a fewer large bodies in the form of planets
Ans. (d)
7. Which of the following two gases were constituent of initial atmosphere ?
a. Helium and Oxygen
b. Hydrogen and helium
c. Hydrogen and nitrogen
d. Hydrogen and oxygen
Ans. (b)
8. What was the nature of initial earth ?
a. A barren, rocky and hot object with a thin atmosphere
b. A barren, rocky and cold object with a dense atmosphere
c. Full of green patches along with rich biodiversity
d. It was composed of all the domains-Atmosphere, lithosphere, hydrosphere and biosphere Ans. (b)
9. Match the items of List I with the items of List II and choose correct answer with the help of given codes.
LIST I (PROCESSES) LIST II (DESCRIPTION)
I. Differentiation - i through which the gases were outpoured from interior
II. Degassing - ii Formation of food by green plants with the help of sunlight
III. Photosynthesis - iii considered the universe to be roughly the same at any point of time
IV. steady state - iv the earth forming material got separated into different layers
Options
I II III IV
a. iv i ii iii
b. i iii ii iv
c. ii iv i iii
d. I ii iii iv
Ans. (a)
10. The present composition of earth’s atmosphere is chiefly contributed by ---------------- and ------------- --.
a. Hydrogen , nitrogen
b. Hydrogen , helium
c. Nitrogen , oxygen
d. Oxygen , helium
Ans. (c)
11. Oceans began to have the contribution of which of the following gases through the process of photosynthesis ?
a. Oxygen
b. Hydrogen
c. Nitrogen
d. Methane
Ans. (a)
12. Consider the following statements regarding the formation of the oceans and choose the correct answer from the options given below
I. The earth’s oceans were formed within 500 million years from the formation of the earth. II. The rainwater falling onto the surface got collected in the depressions to give rise to oceans III. During the cooling of the earth, gases and water vapour were condensed in the interior solid earth.
Options :
a. Only I and II are correct
b. Only I and III are correct
c. Only II and III are correct
d. All are correct
Ans. (a)
13. Which of the following factors contributed water vapour and gases to the atmosphere? a. Continuous seismic activities
b. Continuous rainfall
c. Upliftment of lithosphere
d. Continuous volcanic eruptions
Ans. (d)
14. Consider the following stages of evolution of atmosphere and arrange them according to their correct sequence and choose the correct answer from the options given below i. the hot interior of the earth contributed to the evolution of the atmosphere. ii. the loss of primordial atmosphere.
iii. the composition of the atmosphere was modified by the living world through the process of photosynthesis.
Options:
a. i ii iiii
b. ii i iii
c. iiii ii i
d. ii iii i
Ans. (b
15. Assertion- It can be assumed that life began to evolve sometime 3,800 million years ago.
Reason- The microscopic structures closely related to the present form of blue algae have been found in geological formations much older than some 3,000 million years. Options:
a. Only assertion is correct
b. Only reason is correct
c. Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation for assertion d. Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation for assertion Ans. (c)
16. Life was confined to the ----------------------for a long time
a. Oceans
b. Continents
c. Beneath the earth
d. Between the rocks
Ans. (a)
17. Pick out the correct group of layers of the earth from the surface to the interior from given options a. Mantle, crust, core
b. Crust, core, mantle
c. Crust, mantle, core
d. Core, crust, mantle
Ans. (c)
18. In which of the following units, the distances among galaxies measured ?
a. Kilometers
b. Miles
c. Faithoms
d. Light years
Ans. (d)
19. Who has given the concept of Steady State ?
a. Hoyle
b. Arthur Holmes
c. Carl Ritter
d. Otto Schmidt
Ans. (a)
20. The diameters of individual galaxies range from--------------------light years. a. 80,000-140,000
b. 80,000-150,000
c. 80,000- 160,000
d. 80,000- 145,000
Ans. (b)
L-3 INTERIOR OF THE EARTH
1. The earth’s radius is -------------km.
a. 6370
b. 6730
c. 6307
d. 6073
e. Ans. (a)
2. Consider the following statements regarding the formation of the oceans and choose the correct answer from the options given below
I. The configuration of the surface of the earth is largely a product of the processes operating in the interior of the earth.
II. Exogenic as well as endogenic processes are constantly shaping the landscape. Options :
a. Both I and II are incorrect
b. Both I and II are correct
c. Only II is correct
d. Only I is correct
Ans. (b)
3. The most easily available solid earth material is -------------------------------.
a. Surface water
b. Dust particles
c. Avalanches
d. surface rock
Ans. (d)
4. Which of the following is among the major project lead by scientist to know about the interior of the earth ?
a. Deep land drilling project
b. Deep mining project
c. Integrated Ocean Drilling Project
d. Integrated mining project
Ans. (c)
5. Which of the following forms source of obtaining direct information about the earth’s interior ? a. Volcanic eruption
b. Meteors
c. Magnetic field
d. Seismic activity
Ans. (a)
6. Which of the following is not matched correctly ?
a. Focus - The point where the energy is released
b. Shadow zone - Where all the waves reach
c. Epicentre - The point on the surface nearest to the focus
d. Tsunamis - waves generated by the tremors and not an earthquake in itself Ans. (b)
7. Match the List I with List II and choose correct answer with the help of given codes. LIST I LIST II
I. Richter scale i. The upper portion of the mantle
II. Asthenosphere ii. Mercailli
III. Deccan trap iii. Magnitude scale
IV. Intensity Scale Iv. Flood Basalt Provinces
Options
I II III IV
a. iii i iv ii
b. i iii ii iv
c. ii iv i iii
d. I ii iii iv
Ans. (a)
8. ------------------------- are generated due to the release of energy at the focus and move in all directions. a. Surface waves
b. Body waves
c. P waves
d. Secondary waves
Ans. (b)
9. Which of the following instruments is used to record earthquake ?
a. Barometer
b. Seismograph
c. Hygrometer
d. Anemometer
Ans. (b)
10. Match the column I with column II and choose the correct answer from the options given below COLUMN I COLUMN II
I. Shield volcanoes i. occur in the oceanic areas.
II. Composite volcano ii. largest of all the volcanoes
III. Caldera iii. eruptions with cooler and more viscous lava IV. Flood basalt province iv. highly fluid lava that flows for long distances V. Mid-Ocean Ridge Volcanoes v. most explosive of the earth’s volcanoes Options
I II III IV V
a. iii i iv ii v
b. i iii ii iv v
c. ii iv i v iii
d. ii iii v iv i
Ans. (d)
11. Which of the following statement is not true about the propagation of P-waves of earthquake? a. These waves vibrate parallel to the direction of the wave.
b. They exert pressure on the material in the direction of the propagation
c. They create density differences in the material leading to stretching and squeezing of the material.
d. These waves are considered to be the most damaging waves.
Ans. (d)
12. In which of the following areas, the continental crust is thicker?
a. Plains
b. Oceans
c. Mountains
d. Plateaus
Ans. (c)
13. The core mantle boundary is located at the depth of----------------------------------. a. 2,900 km.
b. 2,800 km
c. 2,700 km
d. 2,600 km
Ans. (a)
14. Which of the following is not matched correctly?
TYPES OF EARHQUAKE CAUSE
a. Tectonic - generated due to sliding of rocks along a fault plane b. Explosion - occur in the areas of large reservoirs
c. Collapse - occur in the areas of mining sites
d. Volcanic - confined to areas of active volcanoes
Ans. (b)
15. The Deccan Trap of India is an example of which of the following kind of volcanic eruptions?
a. Composite volcano
b. Caldera
c. Shield volcano
d. Flood basalt provinces
Ans. (d)
16. In which of the following area, Dykes (intrusive volcanic landforms) are most commonly found a. Eastern Maharashtra
b. Western Maharashtra
c. Rajasthan
d. Malwa plateau
Ans.(b)
17. Which of the following is not an indirect source of information about earth’s interior? a. Magnetic field
b. Seismic activity
c. Volcanic eruption
d. Meteors
Ans. (c)
18. some specific areas where the waves are not reported is called the--------------------. a. Shadow zone
b. Non-seismic area
c. Disappearance zone
d. Zero zone
Ans. (a)
19. Which of the following is the most common types of earthquake?
a. Tectonic earthquake
b. Collapse earthquake
c. Explosion earthquake
d. Reservoir induced earthquake
Ans. (a)
20. Which of the following forms lithosphere?
a. Upper part of crust
b. Crust and the uppermost part of the mantle c. Upper and lower part of crust
d. Lower crust and upper mantle
Ans. (b)
L-4 DISTRIBUTION OF OCEANS AND CONTINENTS 1. Match column I with column II and choose the correct answers with the help of given codes:
Name of scientist Theory/Hypothesis
I. Alfred Wagener - i. Plate tectonics
II. Arthur Homes - ii. Sea floor spreading
III. Mackenzie & Parker - iii. Continental drift theory
IV. Hess - iv. Convectional current theory
Options-
I II III IV
a. ii i iv iii
b. Iv ii i iii
c. i ii iii iv
d. iii iv i ii
Ans. (d)
2. Which of the following scientist was first proposed the possibility of the two Americas, Europe and Africa, to be once joined together?
a. Alfred Wagener
b. Abraham Ortelius
c. Antonio Pellegrini
d. Arthur Holmes
Ans. (b)
3. What was the name of mega ocean according to Wagener?
a. Panthalassa
b. Pangea
c. Gondwanaland
d. Laurasia
Ans. (a)
4. Consider the following Assertion and Reason and choose the correct answer from the options given below
Options:
Assertion :There is the possibility of convection currents operating in the mantle portion. Reason : These currents are generated due to radioactive elements causing thermal differences in the mantle portion.
a. Only assertion is correct
b. Only reason is correct
c. Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation for assertion d. Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation for assertion Ans. (c)
5. Which of the following statement is not true about the ocean configuration ? a. The ocean floor is not just a vast plain but it is full of relief.
b. The submerged mountain ranges as well as deep trenches are found in oceans mostly located closer to the continent margins.
c. The mid-oceanic ridges were found to be most active in terms of volcanic eruptions d. The dating of the rocks from the oceanic crust revealed the fact that they are much older than the continental areas.
Ans. (d)
6. Abyssal plains are found in between the------------------------------------.
a. continental margins and mid-oceanic ridges
b. continental margins and continental slopes
c. Mid oceanic ridges and deep sea trenches
d. Continental margins and deep sea trenches
Ans. (a)
7. Which of the following group depicts the correct order of various parts of Continental margins a. continental shelf, continental rise and deep-oceanic trenches, continental slope b. continental shelf, continental slope, continental rise and deep-oceanic trenches c. continental slope, continental rise and deep-oceanic trenches, continental shelf d. continental rise, continental shelf, continental slope, and deep-oceanic trenches Ans. (b)
8. Which of the following landmasses formed Indian plate?
a. Peninsular India and New Zealand
b. New Zealand and the Australian continental portions
c. Peninsular India and the Australian continental portions
d. Arabian plate and Northern India
Ans. (c)
9. Which of the following event took place during the movement of the Indian plate towards the Eurasian plate ?
a. The outpouring of lava and formation of the Deccan Traps
b. The subcontinent was still close to the equator from 40 million years ago c. Continuous rise in the height of Himalaya
d. Continent convergence
Ans. (a)
10. In which of the following areas, rate of plate movement is very high ?
a. At the arctic ridge
b. Beneath the Himalayan muntains
c. At the Antarctic circle
d. At the East- Pacific rise near Easter island.
Ans. (d)
11. Match column I with column II and choose the correct answers with the help of given codes: COLUMN-I COLUMN-II
I. Spreading sites - i. Where the crust is neither produced nor destroyed
II. Transform boundaries - ii where sinking of a plate occurs I. Subduction zone - iii. Where new crust is generated II. Divergent boundaries - iv. where the plates move away from each other
Options-
I II III IV
a. ii i iv iii
b. iv i ii iii
c. i ii iii iv
d. iii iv i ii
Ans. (b)
12. Consider the following Assertion and Reason and choose the correct answer from the options given below
Assertion : the earth is not a perfect sphere; it has a bulge at the equator.
Reason : This bulge is due to the rotation of the earth.
a. Only assertion is correct
b. Only reason is correct
c. Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation for assertion d. Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation for assertion Ans. (c)
13. Which of the following period added new information to geological literature particularly about sea floor ?
a. The post–World War II
b. The post–World War I
c. The tertiary period
d. The ancient period
Ans. (a)
14. Consider the following statements about the mid oceanic ridges and choose the correct answer from the options given below
I. It is the longest mountain-chain on the surface of the earth though submerged under the oceanic waters.
II. It is characterised by a central rift system at the crest
III. The rift system at the crest is the zone of intense volcanic activity
Options :
a. Only I and II are correct
b. Only I and III are correct
c. Only II and III are correct
d. All are correct
Ans. (d)
15. Which of the following plates considered among the category of minor plate ? a. African plate
b. Cocos plate
c. Pacific plate
d. Eurasian plate
Ans. (b)
16. In which of the following plates, caribbean Islands are included ?
a. Pacific plate
b. North American plate
c. South American plate
d. Antarctica plate
Ans. (c)
17. It was It was realised that all along the--------------- volcanic eruptions are common.
a. Mid-Oceanic ridges
b. Himalayas
c. Islands
d. Hills of Lakshdweep Islands
Ans. (a)
18. Which of the following is not matched correctly ?
a. Cocos plate - Between North America and Pacific plate
b. Nazca plate - Between South America and Pacific plate
c. Arabian plate - Mostly the Saudi Arabian landmass
d. Philippine plate - Between the Asiatic and Pacific plate
Ans. (a)
19. When was the outpouring of lava and formation of the Deccan Traps took place in India? a. At the time of formation of Himalayas
b. During the movement of the Indian plate towards the Eurasian plate. c. At the time of formation of Northern Plains
d. During the movement of Indian plate towards Australia
Ans. (b)
20. Which of the following areas are included in Indian plate ?
a. Peninsular India and New Zealand
b. Peninsular India and South Africa
c. Peninsular India and the Australian continental portion
d. Peninsular India and the Sri Lanka
Ans. (c)
L-5: GEOMORPHIC PROCESSES
1. Which of the following factors have been responsible for the variations in the outer surface of the crust ?
a. The differences in the internal forces operating from within the earth
b. The work and intensity of external forces
c. Weakness of a particular place
d. Human activities
Ans. (a)
2. The phenomenon of wearing down of relief variations of the surface of the earth through erosion is known as ------------------.
a. Levelling
b. Gradation
c. Erosion
d. Deposition
Ans. (b)
3. What stands for soil eluviation ?
a. Downward transportation of soil components due to excess of water
b. Upward movement of water with soil
c. Solidification of kankars by removing extra water
d. Erosion of soil due to excess of water
Ans. (a)
4. Which of the following is not matched correctly ?
a. Desilication - Removal of silica from the soil
b. Slump - slipping of one or several units of rock debris with a backward rotation c. Denudation - strip off or to uncover
d. Pedology - Study of animals
Ans. (d)
5. Consider the following Assertion and Reason and choose the correct answer from the options given below
Assertion : Humus accumulates in cold climates
Reason : bacterial growth is slow
a. Only assertion is correct
b. Only reason is correct
c. Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct
explanation for assertion
d. Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the
correct explanation for assertion
Ans. (c)
6. Which of the following lines best define the word Diastrophism?
a. The process of orogeny
b. All processes that move, elevate or build up portions of the earth’s crust
c. Plate tectonics involving horizontal movements of crustal plates
d. Epeirogenic processes involving uplift or warping of large parts of the earth’s crust Ans. (b)
7. Complete the following diagram by using appropriate terminology.
a. Weathering , Erosion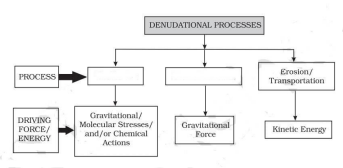 b. Erosion , Denudation
b. Erosion , Denudation
c. Denudation , Mass movement
d. Weathering , Mass movement
Ans. (d)
8. Consider the following Assertion and Reason and choose the correct answer from the options given below
Assertion : Exfoliation domes and tors result due to unloading and thermal expansion respectively Reason : Exfoliation can occur due to expansion and contraction induced by temperature changes a. Only assertion is correct
b. Only reason is correct
c. Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation for assertion d. Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation for assertion Ans. (c)
9. Consider the following causes about mass movement and choose the correct answer from the options given below
I. Removal of support from below to materials above through natural or artificial means II. Increase in gradient and height of slopes
III. Overloading through addition of materials naturally or by artificial filling
IV. Overloading due to heavy rainfall, saturation and lubrication of slope materials V. Excessive natural seepage
OPTION:
a. Only I, II, and IV are true
b. Only II, III, IV and V are true
c. Only I, IV and V are true
d. All are true
Ans. (d)
10. Which of the following not belongs to the group of chemical weathering processes ? a. Exfoliation
b. Carbonation
c. Oxidation
d. Hydration
Ans. (a)
11. Exfoliation belongs to which of the following groups of weathering ?
a. Chemical weathering
b. Biological weathering
c. Physical or mechanical weathering
d. Both Physical and chemical weathering
Ans. (c)
12. Which group of organisms is helpful in biological weathering?
a. Termites, tiger, elephants
b. Earthworms, termites, rodents
c. Rodents, crocodiles, earthworms
d. Earthworms, birds, snakes
Ans. (b)
13. Mass movements transfer the mass of rock debris down the slopes under the direct influence of ------. a. Erosion
b. Gravity
c. Weathering
d. Diastrophism
Ans. (b)
14. Match column I with column II and choose the correct answers with the help of given codes:
COLUMN-I COLUMN-II
I. Slump - i. Removal of silica from the soil
III. Debris slide - ii Sliding of individual rock masses IV. Rockslide - iii. Sliding of earth debris without backward rotation V. Desilication - iv. Slipping of one or several units of rock debris
Options
I II III IV
a. iv iii ii i
b. Iv i ii iii
c. i ii iii iv
d. iii iv i ii
Ans. (a)
15. Which of the following factor is responsible for mass movement ?
a. Gravity
b. Running water
c. Waves
d. Glaciers
Ans. (a)
16. ---------------involves acquisition and transportation of rock debris.
a. Deposition
b. Erosion
c. Gravity
d. Mass movement
Ans. (b)
17. Pedogenesis refers to which of the following processes ?
a. Rock formation
b. Landforms formation
c. Mountain formation
d. Soil formation
Ans. (d)
18. Consider the following Assertion and Reason and choose the correct answer from the options given below
Assertion : Mass movements are very active over weathered slopes rather than over un weathered materials.
Reason : No geomorphic agent like running water, glaciers, wind, waves and currents participate in the process of mass movements.
Options:
a. Only assertion is correct
b. Only reason is correct
c. Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation for assertion d. Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation for assertion Ans. (d)
19. Which of the following factors do not favour mass movements ?
a. Thinly bedded rocks faults
b. Vertical cliffs or steep slopes
c. Lack of precipitation
d. Weak unconsolidated materials
Ans. (c)
20. Denudational processes like erosion and transportation are controlled by ----------------------. a. Kinetic energy
b. Terrestrial radiation
c. Climatic conditions
d. Earth rotation
Ans. (a)
L-6 LANDFORMS AND THEIR EVOLUTION
1. Which of the following is not an agent of erosion ?
a. Running water
b. Glaciers
c. Solar radiation
d. Ground water
Ans. (c)
2. Consider the following Assertion and Reason and choose the correct answer from the options given below
Assertion Several related landforms together make up landscapes.
Reason : Landforms once formed may change in their shape, size and nature slowly or fast Options:
a. Only assertion is correct
b. Only reason is correct
c. Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation for assertion d. Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation for assertion Ans. (d)
3. Match column I with column II and choose the correct answers with the help of given codes
COLUMN I (Geomorphic agents) COLUMN II (Working areas) I. Ground water i Humid region
II. Glaciers ii Arid region
III. Running water iii Limestone region
IV. Wind iv High mountains covered with snow
Options :
I II III IV
a. iii iv i ii
b. i ii iii iv
c. ii iii i iv
d. iv i ii iii
Ans. (a)
4. The term ‘Linear flow’ is associated with which of the following geomorphic agents ? a. Ocean waves
b. Running water
c. Glaciers
d. Ground water
Ans. (b)
5. ‘Waterfalls’ and ‘rapids’ are common in which of the following stages of rivers ? a. Mature
b. Old
c. Youth
d. Deltaic
Ans. (d)
6. By considering following hint, identify the feature created by river
“ A deep valley with very steep to straight sides”
a. Canyon
b. V- shaped valley
c. Gorge
d. Potholes
Ans. (a)
7. Identify the following feature and choose the correct answer from the given options: 
a. Gorge
b. U-shaped valley
c. Grand canyon
d. V- shaped valley
Ans. (c)
8. Match column I with column II and choose the correct answers with the help of given codes
COLUMN I | COLUMN II |
I. | Sink holes | i | 
|
II. | Alluvial fan | ii | 
|
III. | Gorge | iii | 
|
IV. | Sand dunes | iv | 
|
Options :
I II III IV
a. iii iv i ii
b. i i iii iv
c. ii iii i iv
d. iv i ii iii
Ans. (d)
9. Monadnocks and Peneplain are the terms associated with which of the following geomorphic agents ? a. Sea waves
b. Running water
c. Glaciers
d. Ground water
Ans. (b)
10. Following are the processes of formation of a feature given, by considering these processes, identify the feature that made.
❖ These are the most common of landforms in glaciated mountains.
❖ These quite often are found at the heads of glacial valleys.
❖ The accumulated ice cuts these features while moving down the mountain tops. ❖ They are deep, long and wide troughs or basins with very steep concave to vertically dropping high walls at its head as well as sides.
a. Cirques
b. Outwash plains
c. Drumlins
d. Moraines
Ans. (a)
11. Consider the following Assertion and Reason and choose the correct answer from the options given below
Assertion Coastal processes are the most dynamic and hence most destructive.
Reason : When waves break, the water is thrown with great force onto the shore, and simultaneously, there is a great churning of sediments on the sea bottom.
Options:
a. Only assertion is correct
b. Only reason is correct
c. Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation for assertion d. Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation for assertion Ans. (c)
12. In which of the following areas, sea waves break with great force ?
a. Along low beach
b. Along high rocky coasts
c. Along high beach
d. At the smooth coast
Ans. (b)
13. Bars are submerged features and when bars show up above water, they are called----------------------. a. Barrier bars
b. Lagoons
c. Wave-cut platform
d. Off-shore bar
Ans. (a)
14. Which of the following groups purely belong to the erosional landforms created by sea waves ? a. Beaches and dunes
b. Barriers and beaches
c. Spits and dunes
d. Cliffs and caves
Ans. (d)
15. Which of the following landforms are created by winds?
a. Beaches
b. Meanders
c. Playas
d. Caves and stacks
Ans. (c)
16. Which groups of landforms is created by glaciers?
a. Out wash plain, Drumlins, Eskers
b. Cliffs, terraces, caves
c. Pediments, sand dunes, Deflation hollows
d. Caves, sinkholes, Stalactite
Ans. (a)
17. ------------------- are long ridges of deposits of glacial till.
a. Eskers
b. Moraines
c. Drumlins
d. Outwash plains
Ans. (b)
18. Gently inclined rocky floors close to the mountains at their foot with or without a thin cover of debris, are called -------------------------.
a. Beaches
b. Pediments
c. Sea caves
d. Platforms
Ans. (b)
19. Which of the following places are good for the formation of sand dunes ?
a. Dry cold deserts
b. Cold deserts at low heights
c. Dry hot deserts
d. Semi-arid regions
Ans. (c)
20. Which of the following is not matched correctly ?
a. Delta - A depression found in the middle of a river
b. Meanders - Loop like channel pattern
c. Karst topography - The action of ground water in limestone region
d. Potholes - Circular depressions
L.7 - COMPOSITION AND STRUCTURE OF ATMOSPHERE
1. Consider the following Assertion and Reason and choose the correct answer from the options given below-
Assertion: Atmosphere is a mixture of different gases and it envelopes the earth all round. Reason : The air is an integral part of the earth’s mass and 99 per cent of the total mass of the atmosphere is confined to the height of 32 km from the earth’s surface.
Options:
a. Both assertion and reason are correct
b. Only Both assertion and reason are incorrect
c. Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation for assertion d. Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation for assertion Ans. (a)
2. Which of the following gas is considered as greenhouse gas ?
a. Oxygen
b. Ozone
c. Carbon dioxide
d. Methane
Ans. (c)
3. Carbon dioxide and water vapour are found only up to-------------- from the surface of the earth. a. 90 km
b. 100 km
c. 95 km
d. 105 km
Ans. (a)
4. Which of the following gas acts as a filter and absorbs the ultra-violet rays radiating from the sun and prevents them from reaching the surface of the earth?
a. Methane
b. Ozone
c. Oxygen
d. Nitrogen
Ans. (b)
5. Consider the following statements and identify the correct layer on the basis of these statements from the given options.
➢ All changes in climate and weather take place in this layer
➢ The temperature in this layer decreases at the rate of 1°C for every 165m of height. ➢ This is the most important layer for all biological activity.
a. Mesosphere
b. Ionosphere
c. Stratosphere
d. Troposphere
Ans. (d)
6. Consider the following Assertion and Reason and choose the correct answer from the options given below-
Assertion:. The proportion of gases changes in the higher layers of the atmosphere Reason : oxygen will be almost in negligible quantity at the height of 120 km.
.Options:
a. Both assertion and reason are correct
b. Only Both assertion and reason are incorrect
c. Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation for assertion d. Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation for assertion Ans. (c)
7. In the warm and wet tropics, what percent of water vapour found in the air by volume ? a. 4 percent
b. 1 percent
c. 6 percent
d. 3 percent
Ans. (a)
8. Which of the following layers of atmosphere made radio communication possible to us ? a. Troposphere
b. Stratosphere
c. Ionosphere
d. Mesosphere
Ans. (c)
9. Choose the correct order of atmospheric layers from the given option.
a. Stratosphere, Troposphere, Thermosphere, Mesosphere, Exosphere
b. Troposphere, Stratosphere, Mesosphere, Thermosphere, Exosphere
c. Troposphere, Mesosphere, Stratosphere, Exosphere, Thermosphere
d. Troposphere, Exosphere, Stratosphere, Mesosphere, Thermosphere
Ans. (b)
10. Which of the following components of atmosphere act as hygroscopic nuclei around which water vapour condenses to produce clouds ?
a. Meteors
b. Water vapour
c. Gases
d. Dust and salt particles
Ans. (d)
11. Tropopause is the separating zone between-----------------and-------------------------. a. Troposphere, Stratosphere
b. Troposphere, Mesosphere
c. Stratosphere, Mesosphere
d. Troposphere, Exosphere
Ans. (a)
12. The ionosphere is located above which of the following layers ?
a. Stratopause
b. Mesopause
c. Tropopause
d. Exosphere
Ans. (b)
13. Which of the following elements is not related with the elements of weather and climate? a. Precipitation
b. Humidity
c. Atmospheric pressure
d. Altitude
Ans. (d)
14. Which of the following is the highest layer of atmosphere?
a. Stratosphere
b. Mesosphere
c. Exosphere
d. Ionosphere
Ans. (c)
15. The volume of which of the following gas in atmosphere is raising continuously? a. Oxygen
b. Carbon dioxide
c. Nitrogen
d. Methane
Ans. (b)
16. Which of the following pairs of atmospheric layers is important for geographical studies to Geographers ?
a. Troposphere and Stratosphere
b. Troposphere and Ionosphere
c. Ionosphere and Ozonosphere
d. Stratosphere and Ionosphere
Ans. (a)
17. Which of the following is not matched correctly ?
Atmospheric Component Characteristic
a. Stratosphere - Ozone
b. Dust particles - hygroscopic nuclei
c. Ionosphere - Electrically charged particles
d. Water vapour - Filters ultra-violet rays
Ans. (d)
18. Which of the following statements are true about water vapour? choose the correct answer from the given option.
I. Water vapour is a variable gas in the atmosphere, which decreases with altitude. II. Water vapour decreases from the equator towards the poles.
III. It absorbs parts of the insolation from the sun and preserves the earth’s radiated heat. IV. Water vapour absorbs ozone gas.
Options:
a. Only I, II and IV are true
b. Only I, II and III are true
c. Only I and II are true
d. All are true
Ans. (b)
19. Consider the following Assertion and Reason and choose the correct answer from the options given below-
Assertion:. The higher concentration of dust particles is found in subtropical and temperate regions. Reason : Due to dry winds in comparison to equatorial and polar regions
.Options:
a. Both assertion and reason are correct
b. Only Both assertion and reason are incorrect
c. Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation for assertion d. Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation for assertion Ans. (c)
20. On the basis of which of the following elements, atmosphere is divided into five layers
a. Precipitation
b. Humidity
c. Temperature
d. Air pressure
L-8 SOLAR RADIATION, HEAT BALANCE
AND TEMPERATURE
1. What stands for insolation ?
a. Incoming solar radiation on earth
b. Outgoing terrestrial radiation from the earth
c. Absorbed amount of solar energy by clouds
d. Absorbed amount of energy by water vapour
Ans. (a)
2. Which of the following correctly explains the meaning of Perihelion ?
a. When earth is farthest to the sun
b. When earth is nearest to the moon
c. When earth is nearest to the sun
d. When earth is farthest to the moon
Ans. (c)
3. Which of the following factors are strongly responsible for the variation in the amount and intensity of insolation received by an area? Choose the correct answer from the options given below. I. Configuration of land
II. The rotation of earth on its axis
III. The angle of inclination
IV. Cloudiness of an area
Options:
a. Only III and IV
b. Only I, II and III
c. Only II and III
d. All are correct
Ans. (c)
4. Match column I with column II and choose the correct answers with the help of given codes
COLUMN I COLUMN II
I. Perihelion i Reflected amount of radiation from the earth
II. Albedo of the earth ii 3rd January
III. Aphelion iii Incoming solar radiation
IV. Insolation iv 4th July
Options :
I II III IV
a. iii iv i ii
b. ii i iv iii
c. ii iii i iv
d. iv i ii iii
Ans. (b)
5. The long wave radiation is absorbed by the atmospheric gases particularly by ---------------------------. a. Methane
b. Oxygen
c. Nitrogen
d. Carbon dioxide
Ans. (d)
6. Which of the following is not a way of heating of atmosphere ?
a. Condensation
b. Convection
c. Advection
d. Conduction
Ans. (a)
7. --------------------------takes place when two bodies of unequal temperature are in contact with one another, there is a flow of energy from the warmer to cooler body.
a. Advection
b. Convection
c. Conduction
d. Evaporation
Ans. (c)
8. The convective transfer of energy is confined only to which of the following layers of atmosphere? a. Stratosphere
b. Troposphere
c. Mesosphere
d. Ionosphere
Ans. (b)
9. The transfer of heat through horizontal movement of air is called-----------------------------. a. Advection
b. Convection
c. Conduction
d. None of the above
Ans. (a)
10. Consider the following Assertion and Reason and choose the correct answer from the options given below-
Assertion: Maximum insolation is received over the subtropical deserts
Reason : In winter, the middle and higher latitudes receive less radiation than in summer. .Options:
a. Both assertion and reason are correct
b. Only Both assertion and reason are incorrect
c. Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation for assertion d. Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation for assertion Ans. (d)
11. Which of the following wind is the outcome of advection process?
a. Monsoon
b. Sea breeze
c. Loo
d. Mountain valley
Ans. (c)
12. Which of the following clearly explains the meaning of the ‘albedo of the earth’? a. Units of sun’s energy absorbed by the atmosphere
b. 35 units which reflect back to space even before reaching the earth’s surface c. Units absorbed by clouds
d. Reflected amount of heat from the earth surface
Ans. (b)
13. The---------------- is the measurement in degrees of how hot or cold a thing or a place is. a. Temperature
b. Energy
c. Pressure
d. Humidity
Ans. (a)
14. Which of the following is not matched correctly?
a. Normal lapse rate - 6.5°C per 1,000 m.
b. Isotherms - lines joining places having equal temperature. c. Inversion of temperature - Increase in temperature with increasing height d. Air drainage - Flow of wind at the mountains and hills due to gravity Ans. (c)
15. Which of the following conditions is suitable for the inversion of temperature ? a. A long winter night with clear skies
b. A morning having dense fog
c. A day with stormy winds
d. A summer night with strong wind
Ans. (a)
16. In which of the following area, highest range of temperature found ?
a. In European continent
b. In north-eastern part of Eurasian continent
c. In South Africa
d. In New Zealand
Ans. (b)
17. The earth radiates back how many units from the following in the form of terrestrial radiation ? a. 65 units
b. 51 units
c. 48 units
d. 35 units
Ans. (b)
18. Which of the following statements are not true about the terrestrial radiation ? a. The terrestrial radiation heats up the atmosphere from below
b. The long wave radiation or terrestrial radiation is absorbed by the atmospheric gases particularly by greenhouse gases.
c. The terrestrial radiation absorbed by atmosphere finally returned to the space d. Terrestrial radiation from the earth takes place in short waves forms.
Ans. (d)
19. Consider the following Assertion and Reason and choose the correct answer from the options given below-
Assertion: The atmosphere is largely transparent to short wave solar radiation
Reason : The incoming solar radiation passes through the atmosphere before striking the earth’s surface Options:
a. Both assertion and reason are correct
b. Only Both assertion and reason are incorrect
c. Both assertion and reason are correct but not related with each other.
d. Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation for assertion Ans. (c)
20. Which of the following factors is not responsible for the distribution of temperature over earth’s surface? Choose the correct answer from the options given below
I. The latitude
II. The altitude
III. Distance from the sea
IV. Air-masses and ocean currents
Options:
a. I and II
b. II, III and IV
c. III and IV
d. All are responsible Ans. (d)
L-9 ATMOSPHERIC CIRCULATION
AND WEATHER SYSTEM
1. Which of the following statement is not true?
a. Air expands when heated and gets compressed when cooled.
b. Variations in the atmospheric pressure causes the movement of air from high pressure to low pressure
c. Air in horizontal motion is called wind
d. The vertical rising of moist air get warms and forms cloud
Ans. (d)
2. Which of the following units is used to measure atmospheric pressure?
a. Milibar
b. Celsius
c. Farenhite
d. Miligrams
Ans. (a)
3. At sea level the average atmospheric pressure is-----------------------------.
a. 1015.2 mb
b. 1014.2 mb
c. 1013.2 mb
d. 1012.2 mb
Ans. (c)
4. Name the weather instrument which is used to measure atmospheric pressure. a. Thermometer
b. Barometer
c. Hygrometer
d. Anemometer
Ans. (b)
5. Due to --------------- the air at the surface is denser and hence has higher pressure. a. Differences in temperature
b. Sun energy
c. Water
d. Gravity
Ans. (d)
6. Consider the following Assertion and Reason and choose the correct answer from the options given below-
Assertion: Horizontal distribution of pressure is studied by drawing isobars at constant levels. Reason : Isobars are lines connecting places having equal pressure..
.Options:
a. Both assertion and reason are correct
b. Only Both assertion and reason are incorrect
c. Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation for assertion d. Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation for assertion Ans. (d)
7. Which of the following statement is not true?
a. Near the equator the sea level pressure is low and the area is known as equatorial low. b. Along 30° N and 30o S are found the high-pressure areas known as the equatorial highs. c. Further pole wards along 60o N and 60o S, the low-pressure belts are termed as the sub polar lows. d. Near the poles the pressure is high and it is known as the polar high.
Ans. (b)
8. Which of the following factors affect the velocity and direction of wind? Choose the option for correct answer
I. Pressure gradient force
II. Frictional force
III. Gravity
IV. Coriolis force
Options:
a. I, II and IV
b. I, II and III
c. II, III and IV
d. All are true
Ans. (a)
9. What stands for ITCZ?
a. Inter Temperate Controlling Zone
b. Intra Tropical Convergence Zone
c. Inter Tropical Controlling Zone
d. Inter Tropical Convergence Zone
Ans. (d)
10. Which of the following two distinct factors characterised an air mass?
a. Pressure and Temperature
b. Freezing point and dew point
c. Temperature and humidity
d. Dew point and temperature
Ans. (c)
11. Which of the following factors affect the pattern of planetary winds? Choose the correct answers from the following options.
(i) Latitudinal variation of atmospheric heating
(ii) Emergence of pressure belts
(iii) The migration of belts following apparent path of the sun
(iv) The distribution of continents and oceans
(v) The rotation of earth
Options:
a. (i), (ii) and (v)
b. (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
c. (ii), (iii) and (v)
d. All are correct
Ans. (d)
12. Which of the following pairs is not matched correctly?
a. Geostrophic wind - Isobars are not straight controlled by high friction b. Cyclonic circulation - The wind circulation around a low pressure area c. Anti cyclonic circulation - The wind circulation around a high pressure area d. Ferrel cell - Westerlies winds at the surface
Ans. A.
The homogenous surfaces, over which air masses form, are called the ----------------------------. a. Wind region
b. Source region
c. Planetary area
d. None of the above
Ans. (b)
13. Which of the following lines clearly defines front ?
a. When the air remains over a homogenous area for a sufficiently longer time. b. The cool air of the high plateaus and ice fields.
c. The pattern of wind circulation is modified in different seasons due to the shifting of regions of maximum heating.
d. It is the boundary zone between two different air masses when they meet with each other. Ans. (d)
14. Match column I with column II and choose the correct answers with the help of given codes
COLUMN I (Tropical Cyclones) COLUMN II (Areas) I. Cyclones i South China Sea
II. Hurricanes ii Indian Ocean
III. Willy-willies iii Atlantic Ocean
IV. Typhoons iv Western Australia
Options :
I II III IV
a. iii iv i ii
b. ii i iv iii
c. ii iii iv i
d. iv i ii iii
Ans. (c)
15. What do you mean by the ‘landfall’ of the cyclone ?
a. The place where a tropical cyclone crosses the coast
b. The cyclonic systems developing in the mid and high latitude
c. A mature tropical cyclone characterised by the strong spirally circulating wind around the centre d. A well-grown cumulonimbus cloud that produced thunder and lightening
Ans. (a)
16. The tornado over the sea is called---------------------------.
a. Thunderstorm
b. Water spouts
c. Cold front
d. Occluded front
Ans. (b)
17. In which of the following regions, fronts mainly occur ?
a. Equatorial region
b. Subtropical region
c. Polar region
d. Mid latitudinal region
Ans. (d)
18. Which of the following is not a type of front?
a. Water spouts
b. Stationary
c. Occluded
d. Warm front
Ans. (a)
19. Identify the type of front by considering following hint;
‘An airmass which is fully lifted above the land surface’
a. Cold front
b. Warm front
c. Occluded front
d. Stationary front
Ans. (c)
20. What does a region of calm with subsiding air in tropical cyclone called? a. Centre
b. Eye
c. Water spouts
d. Subsidence
Ans. (b)
L-10 WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE
1. Match the column I with column II and choose the correct answers with the help of given codes
COLUMN I COLUMN II
I. Dew Point i The actual amount of water vapour present in atmosphere
II. Sublimation ii Transformation of water vapour into water III. Condensation iii Transformation of water vapour directly into solid form IV. Absolute humidity iv The temperature at which air saturated
Options :
I II III IV
a. iii iv i ii
b. ii i iv iii
c. ii iii i iv
d. iv iii ii i
Ans. (d)
2. Which of the following facts are true about condensation? Choose the correct answer from the given options.
I. Condensation is caused by the loss of heat.
II. In free air, condensation results from cooling around very small particles termed as hygroscopic condensation nuclei.
III. Condensation takes place when the moist air comes in contact with some colder object. IV. Condensation takes place when temperature is close to the maximum point V. Condensation depends upon the amount of cooling and the relative humidity of the air. Options:
a. I, II, IV and V
b. I, II, III and V
c. I, III and V
d. II, III, IV and V
Ans. (b)
3. Which of the following fact is true about the formation of ‘Dew’?
a. Dew point must be above the freezing point
b. Dew point must be below the freezing point
c. When the temperature of an air mass containing a large quantity of water vapour falls all of a sudden
d. All of the above
Ans. (a)
4. On which of the following two basis, condensation can be classified?
a. Temperature and pressure
b. Location and humidity
c. Temperature and location
d. Location and pressure
Ans. (c)
5. Which of the following is not a form of condensation ?
a. Drizzle
b. Mist
c. Fog
d. Dew
Ans. (a)
6. -------------is a mass of minute water droplets or tiny crystals of ice formed by the condensation. a. Frost
b. Smog
c. Mistral
d. Cloud
Ans. (d)
7. Due to which of the following forms of condensation, the visibility becomes poor to zero? a. Frost
b. Fog and mist
c. Clouds
d. Drizzle
Ans. (b)
8. When a sample of air said to be saturated ? Pick out the correct option.
a. The air containing moisture to its full capacity at a given temperature
b. When a specific percentage of moisture present in the atmosphere at a given temperature c. Moisture retaining capacity of air in per unit air
d. All of the above
Ans. (a)
9. Which of the following is not matched correctly ?
FORMS OF
PRECIPITATION CHARACTERISTICS
a. Precipitation - release of moisture after the condensation of water vapour b. Sleet - frozen raindrops and refrozen melted snow-water.
c. Snowfall - Fine drops of rain
d. Hailstones - formed by the rainwater passing through the colder layers Ans. (c)
10. Which of the following is not a type of rainfall ?
a. Convectional rainfall
b. Orographic rainfall
c. Cyclonic rainfall
d. Plutonic rainfall
Ans. (d)
11. Identify the form of precipitation by using following hint.
‘Moisture is released in the form of hexagonal crystals when the temperature is lower than the 0॰C’ a. Hailstones
b. Snowfall
c. Rainfall
d. Sleet
Ans. (b)
12. Which of the following clouds are formed at high altitude and always look white in colour? a. Cirrus
b. Cumulus
c. Stratus
d. Nimbus
Ans. (a)
13. Match the column I with column II and choose the correct answers with the help of given codes
COLUMN I COLUMN II
(Types of Clouds) (Characteristics)
I. Cirrus i Extremely dense and opaque to sun rays II. Stratus ii Thin and detatched having a feathery appearance III. Nimbus iii Look like cotton wool
IV. Cumulus iv Layered clouds covering large portion of the sky
Options :
I II III IV
a. iii iv i ii
b. ii iv i iii
c. ii iii i iv
d. iv iii ii i
Ans. (b)
14. Which of the following statements are true about the world distribution of rainfall? Choose the correct answer with the help of given options.
I. As we proceed from the equator towards the poles, rainfall goes on decreasing steadily. II. The coastal areas of the world receive greater amounts of rainfall than the interior of the continents.
III. The rainfall is more over the oceans than on the landmasses of the world because of being great sources of water.
IV. Between the latitudes 350 and 400 N and S of the equator, the rain is scanty on the eastern coast.
Options:
a. I, II and IV
b. II, III and IV
c. I, II and III
d. III and IV
Ans. (c)
15. In which of the following regions, rainfall is distributed evenly throughout the year? a. The equatorial belt
b. The eastern part of cool temperate regions
c. The northern parts of all continents
d. The western part of tropical region
Ans. (a)
16. Consider the following Assertion and Reason and choose the correct answer from the options given below-
Assertion: The rainfall is more over the oceans than on the landmasses of the world. Reason : Oceans are the great sources of water.
Options:
a. Both assertion and reason are correct
b. Only Both assertion and reason are incorrect
c. Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation for assertion d. Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation for assertion Ans. (c)
17. The area situated on the leeward side, which gets less rainfall is known as the-------------------------. a. Relief rain
b. Humid region
c. Arid region
d. rain-shadow area
Ans. (d)
18. between 45॰ and 65॰ N and S of equator, due to the westerlies, the rainfall is first received on which part of the continents?
a. On eastern margins
b. On western margins
c. On northern margins
d. On southern margins
Ans. (b)
19. Consider the following Assertion and Reason and choose the correct answer from the options given below-
Assertion:. The leeward slopes remain rainless and dry.
Reason : The area situated on the leeward side, gets less rainfall and known as the rain-shadow area. Options:
a. Both assertion and reason are correct but not related to each other
b. Only Both assertion and reason are incorrect
c. Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation for assertion d. Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation for assertion Ans. (a)
20. Which of the following point is correctly depict the term ‘latent heat of vapouraisation’ a. The transformation of water vapour into water
b. Condensation of water directly into ice
c. The temperature at which the water starts evaporating
d. The air containing moisture to its full capacity
Ans. (c)
21. What percentage of water vapour by volume we found in the atmosphere?
a. Zero to four percent
b. Two to three percent
c. Zero to three percent
d. Zero to two percent
Ans. (a)
L-11 WORLD CLIMATE AND CLIMATE CHANGE
1. Which of the following is not an approach adopted for classifying climate ?
a. Empirical
b. Genetic
c. Applied
d. Observational
Ans. (d)
2. The most widely used classification of climate is the-------------- climate classification scheme developed by----------------------------.
a. Applied, Thornwaite
b. Genetic, V. Koeppen
c. Empirical, V. Koeppen
d. None of the above
Ans. (c)
3. Which of the following two elements were taken by Koeppen to schematised the world’s climate ? a. Temperature and Vegetation
b. Temperature and Precipitation
c. Precipitation and Vegetation
d. Temperature and Pressure
Ans. (b)
4. How many climatic groups were based on precipitation as recognised by V. Koeppen. a. One
b. Four
c. Three
d. Two
Ans. (a)
5. According to Koeppen’s climatic scheme, letter ‘B’ denotes which of the following types of climate? a. Tropical
b. Dry climates
c. Warm temperate
d. Cold climates
Ans. (b)
6. Match the letters (Column I) used by Koeppen to schematised world climate with their climatic groups (Column II) and choose the correct answers with the help of given codes
COLUMN I (LETTERS) COLUMN II (CLIMATIC GROUPS) I. A i Cold climates
II. C ii High Land
III. D iii Warm Temperate
IV. E iv Tropical climates
V. H v Cold snow forest climates
Options :
I II III IV V
a. iii iv i ii v
b. ii i iv v iii
c. ii iii i v iv
d. iv iii v i ii
Ans. (d)
7. Which of the following is not matched correctly ?
SUB DIVISION CLIMATE TYPE
a. Am - Tropical Monsoon Climate
b. Cwa - Humid Subtropical Climate
c. Af - Mediterranean Climate
d. Cfa - Humid Subtropical Climate
Ans. (c)
8. In which of the following area, tropical monsoon type climate is not found ? a. Indian sub-continent
b. Central California
c. North Eastern part of South America
d. Northern Australia
Ans. (b)
9. Following characteristics are found in which type of climate ?
➢ Hot, dry summer and mild, rainy winter.
➢ Monthly average temperature in summer is around 25° C and in winter below 10°C. ➢ The annual precipitation ranges between 35 - 90 cm.
a. Mediterranean Climate
b. Humid Subtropical Climate
c. Tropical Wet Climate
d. Tropical Monsoon Climate
Ans. (a)
10. Which of the following clearly explains the meaning of greenhouse effect?
a. Concentration point of GHGs
b. The processes that warm the atmosphere
c. The gases that absorb long wave radiation
d. The transmission of incoming solar radiation into space
Ans. (b)
11. Which of the following years was observed the warmest year of the 20th century? a. 1991
b. 1995
c. 1998
d. 1999
Ans. (c)
12. What was the limit of carbon dioxide emission was bound by the Kyoto protocol for 35 industrialised countries till 2012 ?
a. 7 percent
b. 3 percent
c. 4 percent
d. 5 percent
Ans. (d)
13. Which of the following gas is not included in the category of GHGs (Green House Gases) ? a. Carbon dioxide
b. Sulphur dioxide
c. Chlorofluorocarbons
d. Nitrous oxide
Ans. (b)
14. Consider the following Assertion and Reason and choose the correct answer from the options given below-
Assertion: Ozone occurs in the stratosphere.
Reason : Ultra-violet rays convert oxygen into ozone in stratosphere. Thus ultra violet rays do not reach the earth’s surface.
Options:
a. Both assertion and reason are correct but not related to each other
b. Only Both assertion and reason are incorrect
c. Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation for assertion d. Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation for assertion Ans. (c)
15. Consider the following Assertion and Reason and choose the correct answer from the options given below-
Assertion: The CFCs which drift into the stratosphere destroy the ozone.
Reason : Large depletion of ozone occurs over Antarctica.
Options:
a. Both assertion and reason are correct but not related to each other
b. Only Both assertion and reason are incorrect
c. Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation for assertion d. Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation for assertion Ans. (d)
16. Which of the following facts are related with Global warming. Choose the correct answer from the given options.
I. The effect of global warming may not be uniform everywhere.
II. Rise in the sea level due to melting of glaciers and ice-caps
III. Thermal expansion of the sea may inundate large parts of the coastal area and islands IV. Lack of fishing grounds
Options:
a. I, II and IV
b. II, III and IV
c. I, II and III
d. All are related
Ans. (c)
17. The largest concentration of GHGs in the atmosphere is --------------------------. a. Carbon dioxide
b. Chlorofluorocarbons
c. Nitrous oxide
d. Carbon monoxide
Ans. (a)
18. Which of the following is not associated with the astronomical causes of climate change ? a. Sunspots activities
b. Volcanism
c. Millankovitch oscillations
d. The wobbling of the earth and the change in the earth’s axial tilt
Ans. (b)
19. Which of the following options correctly implies the meaning of sunspots ?
a. Hot points available on sun’s surface
b. Light and hot patches on the sun
c. Dark and cooler patches on the sun
d. Cool transparent points on the sun
Ans. (c)
20. What happens if the sunspots increases ?
a. cooler and wetter weather and greater storminess occur.
b. warm and drier conditions prevail
c. Hot humid conditions occur
d. Cooler and dry conditions occur
Ans. (a)
21. In which of the following climatic regions, the condition of permafrost found where the subsoil is permanently frozen ?
a. Ice cap climate
b. Cold climate with humid winters
c. Marine west coast climate
d. Tundra climate
Ans. (d)
22. In which of the following types of climate, vertical zonation of layering of climatic types found ? a. Tundra climate
b. Highland climates
c. Cold snow forest climates
d. Polar climates
Ans. (b)
L-12 WATER (OCEANS)
1. About what percent of the planetary water is found in the oceans ?
a. 71 Percent
b. 78 Percent
c. 74 Percent
d. 95 Percent
Ans. (a)
2. Which of the following is the shallowest part of the oceans?
a. The Deep sea plain
b. The Oceanic deeps
c. The continental shelf
d. The continental slope
Ans. (c)
3. Which of the following region has the largest continental shelf in the world? a. Coasts of Chile
b. The west coast of Sumatra
c. The eastern coast of India
d. The Siberian shelf in the Arctic Ocean
Ans. (d)
4. Which of the following features of the oceans possess the flattest and smoothest regions of the world ?
a. Oceanic deeps or trenches
b. Deep sea plain
c. Submarine canyons
d. Mid-Oceanic ridges
Ans. (b)
5. Match the column I with column II and choose the correct answers with the help of given codes
COLUMN I COLUMN II
(Types of Clouds) (Characteristics)
I. Atoll i Mountain with pointed summit under sea water II. Seamount ii Deep sea valleys found cutting across the continental shelves III. Guyots iii A flat topped seamount
IV. Submarine Canyon iv Low islands found in the tropical oceans consisting of coral reefs
Options :
I II III IV
a. iii iv i ii
b. ii iv i iii
c. iv i iii ii
d. iv iii ii i
Ans. (c)
6. Which of the following factors don’t affect the temperature of ocean water? a. Altitude
b. Unequal distribution of land and water
c. Prevailing wind
d. Ocean currents
Ans. (a)
7. Consider the following Assertion and Reason and choose the correct answer from the options given below-
Assertion: The winds blowing from the land towards the oceans drive warm surface water away form the coast resulting in the upwelling of cold water from below.
Reason : Movement of water due to winds result into the longitudinal variation in the temperature. Options:
a. Both assertion and reason are correct but not related to each other
b. Only Both assertion and reason are incorrect
c. Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation for assertion d. Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation for assertion Ans. (c)
8. Consider the following points regarding the temperature distribution of oceans. Choose the right answer from the options given below.
I. The oceans in the northern hemisphere receive more heat due to their contact with larger extent of land.
II. The temperature of surface water decreases from the equator towards the poles III. Warm ocean currents raise the temperature in cold areas while the cold currents decrease the temperature in warm ocean areas.
IV. Prevailing wind creates the longitudinal variation in the temperature
Options:
a. I, II and IV
b. II, III and IV
c. I, II and III
d. All are true
Ans. (d)
9. The boundary region, from where there is a rapid decrease of temperature in ocean, is called the------- -----.
a. Anticline
b. Thermocline
c. Syncline
d. Boundary line
Ans. (b)
10. Consider the following Assertion and Reason and choose the correct answer from the options given below-
Assertion: The maximum temperature of the oceans is always at their surfaces. Reason : Oceans directly receive the heat from the sun and the heat is transmitted to the lower sections of the
oceans through the process of convection.
Options:
a. Both assertion and reason are correct but not related to each other
b. Only Both assertion and reason are incorrect
c. Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation for assertion d. Both assertion and reason are correct and reason the correct explanation for assertion Ans. (d)
11. -------------- is the term used to define the total content of dissolved salts in sea water. a. Salinity
b. Alkalinity
c. Temperature
d. Halocline
Ans. (a)
12. Which of the following statement is false regarding the salinity of ocean water ? a. The salinity of water in the surface layer of oceans depend mainly on evaporation and precipitation b. In polar regions, highest salinity found in oceans
c. Surface salinity is greatly influenced in coastal regions by the fresh water flow from rivers d. Wind influences salinity of an area by transferring water to other areas.
Ans. (b)
13. Which of the following value is considered as the upper limit to ‘brackish water’ ? a. 22.7 gms/1000gms sea water
b. 21.7 gms/1000gms sea water
c. 24.7 gms/1000gms sea water
d. 23.7 gms/1000gms sea water
Ans. (c)
14. Which of the following factors is responsible for the salinity variation in the Pacific Ocean? a. Its deepness and large size
b. Its vastness and large area
c. Its quantity of water
d. Its shape and larger areal extent
Ans. (d)
15. Which of the following water bodies containing highest salinity?
a. Lake Van in Turkey
b. Great salt lake
c. Black sea
d. Caspian sea
Ans. (a)
16. Arrange the following water bodies in ascending order in terms of salt content found in them. Choose the correct answer from the options given below
i. Dead Sea
ii. Lake Van
iii. Great Salt Lake
a. i, ii, iii
b. ii, i, iii
c. iii, i, ii
d. ii, iii, i
Ans. (b)
17. Which of the following factors is responsible for the low salinity trend in the Bay of Bengal? a. Due to high evaporation and low influx of fresh water
b. Due to small size
c. Due to influx of river water
d. Due to low evaporation
Ans. (c)
18. Name the zone where salinity increases sharply in the oceans
a. Thermocline
b. Anticline
c. Syncline
d. Halocline
And. (d)
19. Which of the following factors affect the nature of salinity. Choose the correct answer from the options given below ?
I. Salinity at the surface increases by the loss of water to ice or evaporation, or decreased by the input of fresh waters.
II. The lower salinity water rests above the higher salinity dense water that leads to stratification by salinity.
III. Increasing salinity of seawater causes its density to increase
Options:
a. I, II
b. II, III
c. I, III
d. All I, II and III
Ans. (d)
20. Consider the following Assertion and Reason and choose the correct answer from the options given below-
Assertion: Salinity at depth is very much fixed.
Reason : There is no way that water is ‘lost’, or the salt is ‘added.
Options:
a. Both assertion and reason are correct but not related to each other
b. Both assertion and reason are incorrect
c. Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation for assertion d. Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation for assertion Ans. (c)
L-13 MOVEMENTS OF THE OCEAN WATER
1. Which of the following is a horizontal motion of water?
a. Tides
b. Ocean currents
c. Prevailing winds
d. Upwelling of cold water from subsurface
Ans. (b)
2. The movement of which of the following is actually a form of energy not the water? a. Waves
b. Tides
c. Ocean currents
d. Sinking of surface water
Ans. (a)
3. Consider the following Assertion and Reason and choose the correct answer from the options given below-
Assertion: The motion of the surface water seldom affects the stagnant deep bottom water of the oceans. Reason : This is due to the friction occurring between the dynamic water and the sea floor. Options:
a. Both assertion and reason are correct but not related to each other
b. Both assertion and reason are incorrect
c. Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation for assertion d. Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation for assertion Ans. (c)
4. Which of the following points clearly explains the meaning of a ‘Tide’?
a. These are the horizontal motion of water
b. The periodical rise and fall of the sea level, once or twice a day
c. They represent a regular volume of water in a definite path and direction
d. These are differences in water density
Ans. (b)
5. Study the given diagram carefully and fill the blank with appropriate word given in the options below. 
a. Ebb
b. Tidal currents
c. Surges
d. Tidal bulge
Ans. (d)
6. Which of the following is the main reason behind creating surges in ocean waters? a. Due to meteorological effects such as winds and atmospheric pressure changes b. Due to the gravitational attraction of the moon and the centrifugal force
c. Due to the attraction of moon
d. None of the above
Ans. (a)
7. Which of the following is characterised as Semi-diurnal tides?
a. One high tide and one low tide during each day
b. Tides having variations in height
c. Two high tides and two low tides each day
d. Seven days interval between two tides
Ans. (c)
8. Which of the following point correctly depict the meaning of ‘Perigee’?
a. when the moon is farthest from earth
b. when the moon’s orbit is closest to the earth
c. When the earth is closest to the sun
d. When the earth is farthest from the sun
Ans. (b)
9. Which of the following conditions prevails on 4thJuly ?
a. Perigee
b. Apogee
c. Perihelion
d. Aphelion
Ans. (d)
10. On which of the following day, high tide observed?
a. On new moon
b. When the sun and moon are at right angles
c. When the earth is closest to the sun
d. When the moon is closest to the earth
Ans. (a)
11. Consider the following Assertion and Reason and choose the correct answer from the options given below-
Assertion: The tides can be predicted well in advance.
Reason : Tides help the navigators and fishermen to plan their activities.
Options:
a. Both assertion and reason are correct but not related to each other
b. Both assertion and reason are incorrect
c. Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation for assertion d. Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation for assertion Ans. (a)
12. Which of the following primary forces are responsible for the origin of ocean currents? Choose the correct answer from the options given below ?
(i) heating by solar energy;
(ii) wind;
(iii) gravity;
(iv) coriolis force
(v)Water density
Options:
a. (i), (ii) and (v)
b. (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
c. (i), (ii) and (iii)
d. (i) and (iii) only
Ans. (b)
13. Consider the following Assertion and Reason and choose the correct answer from the options given below-
Assertion: Near the equator the ocean water is about 8 cm higher in level than in the middle latitudes. Reason : Heating by solar energy causes the water to expand
Options:
a. Both assertion and reason are correct but not related to each other
b. Both assertion and reason are incorrect
c. Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation for assertion d. Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation for assertion Ans. (c)
14. -----------------tends to pull the water down the pile and create gradient variation. a. Gravity
b. Ocean currents
c. Coriolis force
d. Wind
Ans. (a)
Note : Study the map given below and choose the correct answers of question numbers from 15 to 19. 15. Cold currents are usually found on the-------------------- of the continents in the low and middle  latitudes.
latitudes.
a. South coast
b. North coast
c. East coast
d. west coast
Ans. (d)
16. warm currents bring warm water into cold water areas and are usually observed on the--------------- of continents in the low and middle latitudes
a. East coast
b. West coast
c. North coast
d. South coast
Ans. (a)
17. Which of the following currents belongs to Indian Ocean?
a. Canaries current
b. Humboldt(Peru) current
c. Agulhas current
d. Gulf stream
Ans. (c)
18. Choose the warm ocean currents from the options given below
I. Gulf stream
II. Kuroshio current
III. Labrador current
IV. North Atlantic drift
V. Benguela current
Options:
a. I, II and V
b. I, II and IV
c. I, IV and V
d. All
Ans. (b)
19. Which of the following is not matched correctly
OCEAN CURRENTS OCEAN IN WHICH FOUND
a. Gulf stream - Atlantic ocean
b. Agulhas current - Indian ocean
c. Oyashio current - Pacific ocean
d. California current - Atlantic ocean
Ans. (d)
20. Which of the following statement is not true about the ocean currents ?
a. In regions of pronounced monsoonal flow, the monsoon winds influence the current movements. b. The oceanic circulation transports heat from one latitude belt to another in a manner similar to the heat transported by the general circulation of the atmosphere.
c. Ocean currents bring huge amount of fishes with their flow
d. The mixing of warm and cold currents help to replenish the oxygen and favour the growth of planktons, the primary food for fish population
Ans. (c)
L-14 BIODIVERSITY AND CONSERVATION
1. The basic cause for weathering variations and resultant biodiversity is the input of ----------- and ----------
a. Solar energy, water
b. Solar energy, photosynthesis
c. Photosynthesis, Water
d. Photosynthesis, Carbon cycle
2. Consider the following Assertion and Reason and choose the correct answer from the options given below-
Assertion: Biodiversity is not found evenly on the earth.
Reason : Biodiversity is consistently richer in the tropics.
Options:
a. Both assertion and reason are correct but not related to each other
b. Both assertion and reason are incorrect
c. Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation for assertion d. Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation for assertion Ans. (b)
3. Which of the following facts is not true about biodiversity ?
a. Biodiversity is the number and variety of organisms found within a specified geographic region. b. It refers to the varieties of plants, animals and micro-organisms, the genes they contain and the ecosystems they form.
c. It relates to the similarity among living organisms on the earth, including the similarity within and between the species.
d. It is a result of hundreds of millions of years of evolutionary history.
Ans. (c)
4. Which of the following regions is rich in biodiversity?
a. Tropical
b. Temperate
c. Polar
d. Mid-latitudinal region
Ans. (a)
5. Which of the following is not considered as a level of biodiversity in the world ? a. Genetic diversity
b. Species diversity
c. Ecosystem diversity
d. Scientific diversity
Ans. (d)
6. Groups of individual organisms having certain similarities in their physical characteristics are called------ -----.
a. Species
b. Ecosystem
c. Biosphere
d. None of the above
Ans. (a)
7. Consider the following Assertion and Reason and choose the correct answer from the options given below-
Assertion: Human beings are different in their characteristics such as height, colour, physical appearance, etc., considerably.
Reason : This is due to genetic diversity and this genetic diversity is essential for a healthy breeding of population of species
Options:
a. Both assertion and reason are correct but not related to each other
b. Both assertion and reason are incorrect
c. Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation for assertion d. Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation for assertion Ans. (c)
8. Which of the following is true about the ‘species diversity’?
a. It refers to the variation of genes within species.
b. It relates to the number of species in a defined area.
c. That means, every organism, besides extracting its needs, also contributes something of useful to other organisms
d. It is essential for a healthy breeding of population of species
Ans. (b)
9. Which of the following is a serious ill effect of loss of species?
a. Species capture and store energy
b. Species produce and decompose organic materials
c. Help to cycle water and nutrients throughout the ecosystem
d. It would decrease the ability of the system to maintain itself
Ans. (d)
10. Which of the following is related to ‘crop diversity’?
a. Manufacture of food
b. Pharmaceutical
c. Cosmetic products
d. Production of timber
Ans. (a)
11. How the biodiversity affects the world negatively while it plays economic role? Choose the correct option.
a. The concept of biological resources is responsible for the deterioration of biodiversity. b. The origin of new conflicts dealing with rules of division and appropriation of natural resources. c. The demand is more than the availability of resources
d. All of the above
Ans. (b)
12. Species which are not the natural inhabitants of the local habitat but are introduced into the system, are
called----------------------.
a. Endemic species
b. Rare species
c. Exotic species
d. Extinct species
Ans. (c)
13. Which of the following is not a natural cause of loss of biodiversity ?
a. Earthquakes
b. Volcanic eruptions
c. Droughts
d. Deforestation
Ans. (d)
14. Which of the following groups of animals are always remain the main target of poachers that rendered them in endangered category ?
a. Tigers, elephants, rhinoceros, crocodiles
b. Monkeys, Hyenas, Antelopes, Yak
c. Lion, Horses, Bears, Red Panda
d. Crocodiles, snakes, bears, deer
Ans. (a)
15. What stands for IUCN ?
a. International United Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources
b. International Union Council of Nature and Natural Resources
c. International Union of Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources
d. International United Corporation of Nature and Natural Resources
Ans. (c)
16. Consider the following Assertion and Reason and choose the correct answer from the options given below-
Assertion: Biodiversity is important for human existence
Reason : All forms of life are so closely interlinked that disturbance in one gives rise to imbalance in the others.
Options:
a. Both assertion and reason are correct but not related to each other
b. Both assertion and reason are incorrect
c. Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation for assertion d. Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation for assertion Ans. (c)
17. Which of the following was the main aim of enacting Wild Life Protection Act, 1972? a. To kept them in national parks and zoos for their protection
b. To protect, preserve and propagate the variety of species within natural boundaries c. To give them legal protection
d. To increase their population by providing them safe and protective environment Ans. (b)
18. Which of the following groups of countries possess the Mega diversity Centres of the world a. U.S.A., France, China, Germany
b. Germany, New Zealand, France, Equador
c. Malaysia, Russia, Ukraine, Nepal
d. Brazil, Columbia, India, Mexico
Ans. (d)
19. Hotspots are defined according to their -------------------.
a. Vegetation
b. Rainfall
c. Animals
d. Variety of biological resources
Ans. (a)
20. Which of the following statements are true regarding biodiversity? Choose the right answers from the given options:
i. Most, but not all, of the hotspots rely on species-rich ecosystems for food, firewood, cropland, and income from timber.
ii. Plants are important because these determine the primary productivity of an ecosystem. iii. Main concentration of mega diversity centres is found in Mid latitudinal areas iv. The islands of Hawaii have many unique plants and animals that are threatened by introduced specie.
Options:
a. i, iii, iv
b. i, ii, iv
c. i, ii, iii
d. ii and iii
Ans. (b)

L-1 INDIA – LOCATION
1. Which of the following latitude extensions is relevant in terms of the expansion of the entire land of India?
(A) 8°41′N से 35°7′ N
(B) 8°4′ N से35°6′ N
(C) 8°4′ N से37°6′ N
(D) 6°45′ N से37°6′ N
Ans. (D) 6°45′ N to 37°6′ N
2. What is the total area of India?
(A) 32.8 thousand sq km
(B) 24.6 lakh sq km
(C) 32.8 lakh sq km
(D) 3200 sq km.
Ans. (C) 32.8 sq. km
3. The geographical area of India is what percentage of the geographical area of the world? (A) 32.8%
(B) 8.4%
(C) 2.4%
(D) 4.2%
Ans (C) 2.4%
4. India is spread between how many latitudes and longitudes?
(A) nearly 30
(B) nearly 25
(C) nearly 40
(D) nearly 20
Ans :- (A) nearly 30
Explanation:-
5. If you travel from Rajasthan to Nagaland in a straight line, which one of the following rivers will you not cross?
(A) Yamuna
(B) Indus
(C) Brahmaputra
(D) Ganga
Ans :- (B) Indus
6. Which of the following countries has the longest terrestrial border with India?
(A) Bangladesh
(B) Pakistan
(C) China
(D) Myanmar
Answer:- (A) Bangladesh
7. What is the length of India's maritime boundary line including islands? (A) 6,100 km.
(B) 7,516.6 km.
(C) 15,200 km.
(D) 22,716.6 km.
Ans :- (B) 7,516.6 km.
8. Which of the following is the standard meridian (longitude) of India? (A) 68°7′ eastern longitude
(B) 97°25′ eastern longitude
(C) 82°30′ eastern longitude
(D) 82°30′ eastern longitude
Ans :- (C) 82°30′ eastern longitude
9. Tropic of Cancer does not passes through which of the following group of states ? (A) Gujarat and West Bengal
(B) Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh
(C) Jharkhand and Tripura
(D) Maharashtra and
Orissa
Ans. (D)
10. When did Telangana become the 29th state of India ?
(A) June 2014
(B) November 2014
(C) April 2016
(D) May 2015
Ans:- June 2014
11. Which of the following countries is smaller than India in area ? (A) Russia
(B) United States
(C) Sri Lanka
(D) Brazil
Answer:- (C) Sri Lanka
12. What is the total length of India from north to south?
(A) 2933 km.
(B) 3214 km.
(C) 7516 km.
(D) 15200
km.
Ans :- (B) 3214 km.
13. What is the number of States in India at
present?
(A) 28 (B) 29 (C) 27 (D) 35
Ans:- (A) 28
14. India is located to the north of which of the ocean?
(A) Pacific Ocean
(B) Arctic Sea
(C) Atlantic Ocean
(D) Indian Ocean
Answer:- (D) Indian Ocean
15. Which of the following is not relevant to the benefit of India's position at the heart of Indianocean?
(A) Natural Security
(B) Expansion of Indian Culture
(C) Expansion of Trade Relations
(D) Catching of fishes
Answer:- (D)Catching of fishes
16. Which is the largest state in India by area?
(A) Uttar Pradesh
(B) Madhya Pradesh
(C) Rajasthan
(D) Bihar
Ans.:- (C)Rajasthan
17. Which of the following is a Union Territory located on the west coast of India? (A) Daman Diu and Dadar Nagar Haveli
(B) Laddakh
(C) Andaman and Nicobar Island Groups
(D) Chandigarh
Answer:- (A) Daman Diu and Dadar Nagar Haveli
18. Which of the following countries is larger than India in area?
(A) China
(B) France
(C) Egypt
(D) Iran
Ans :- (B)China
20. Which of the following is the easternmost longitude of India ?
(A) 97°25′ E
(B) 77°6′ E
(C) 68°7′ E
(D) 77°6′ E
Ans :- (A) 97°25′ E
21.The borders of Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, West Bengal and Sikkim meets which of thefollowing country?
(A) China
(B) Bhutan
(C) Nepal
(D) Myanmar
Answer:- (C) Nepal
22. In the summer vacation, if you want to go to Kavaratti, which Union Territory will you go to? (A) Andaman and Nicobar
(B) Daman and Diu
(C) Puducherry
(D) Lakshadweep
Answer:- (D) Lakshadweep
23.Our friends are residents of a country which does not border India. Please tell me the name of that country from the following?
(A) Bangladesh
(B) Nepal
(C) Tajikistan
(D) Bhutan
Answer:- (C) Tajikistan
24.Which of the following countries is not included in the Indian subcontinent? (A) Pakistan
(B) Bangladesh
(C) Myanmar
(D) Bhutan
Answer:- (C)
Myanmar
25.How far ahead or behind Indian standard time from 'Greenwich' Mean time? (A) 5 hours 30 minutes behind
(B) 5 hours 30 minutes ahead
(C) 4 hours 30 minutes ahead
(D) 4 hours 30 minutes behind
Answer:- (B) 5 hours 30 minutes aheadt
26. Which of the following is a pass located in Himalayas (A) Nathula
(B) Bhorghat
(C) Aravali
(D) Shiwalik
Answer:- (A)
Nathula
27.Which of the following states has the longest coastline in India? (A) Maharashtra
(B) Andhra Pradesh
(C) Tamil Nadu
(D) Gujarat
Ans. (D)
Gujarat
28.What is the southernmost end of the mainland of India?
(A) Chennai
(B) Kumari Antreep
(C) Port Blair
(D) Kavaratti
Answer:- (B) Kumari Antareep
MAP BASED QUESTIONS
1. Which of the following states of India has the longest coastline ? a. Andhra Pradesh
b. Gujarat
c. Tamil Nadu
d. Maharashtra
Ans. (b)
2.Which of the following states is not included in the group of seven north-eastern most states?
a. West Bengal
b. Assam
c. Arunachal Pradesh
d. Manipur
Ans. (a)
3. Which of the following states does not share international border with China ?
a. Sikkim
b. Uttaranchal
c. Arunachal Pradesh
d. Nagaland
Ans. (d)
4. Which is the largest state in India in terms of area shared ?
a. Maharashtra
b. Rajasthan
c. Madhya Pradesh
d. Karnataka
Ans. (b)
5. Name the state where Thar desert is found ?
a. Andhra Pradesh
b. Gujarat
c. Tamil Nadu
d. Rajasthan
Ans, (d)
Study the map of India carefully and answer the questions given below
1. Which of the following longitudes has been selected as the standard meridian for India? a. 82ᵒ 30’ E
b. 8ᵒ 4’ E
c .89ᵒ 32’ E
d . None of the above
Ans. (a)
2. What is the total length of the beach for the entire Indian land?
a. 7517 K.M.
b. 6100 K.M.
c. 7500 K.M.
d. 6517 K.M.
Ans. (a)
3. Which of the following is not a neighbour of India located in the North-East? a. China
b. Bangladesh
c. Bhutan
d. Pakistan
Ans. (d)
4. Which is the far easternost meridian of India?
a. 68० 7’ E b. 97० 25’ E
c. 97० 8’ E d. 36० 7’ E
Ans. (b)
5. What is the north-southern extension of India?
a. 3214 Kilometer
b. 2933 km
c. 3412 km
d. 2393 km
Ans. (a)
SOME MORE QUESTIONS
1 . Being a large geographical unit, India is also called the subcontinent, which of the following countries does not join the Indian subcontinent?
a.Nepal
a. Bhutan
b. China
c. Bangladesh
Ans. (b)
2. India is located in---------------------- part of the Asian continent?
a. Southern
b. South-East
c. East-West
d. South-West
Ans. (a)
3. Which of the following physical forms separates Sri Lanka and India?
a. Bay of Bengal and Palk Strait
b. Gulf of Mannar and Palk Strait
c. Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea
d. Arabian Sea and Palk Strait
Ans. (b)
4 . Which of the following rivers is not related to India?
a. Ganga
b. Brahmaputra
c. Godavari
d. Nile
Ans. (d)
5 . What is the difference of about how many hours is seen in the time of the easternmost and westernmost parts of our country?
a. 1 hour 50 min
b. 2 hours 10 min
c. 2 hours
d. 1 hour 30 min
Ans. (c)
6 . India's latitude and longitude extension is about 30०, while its actual distance from north to south is 3214 km. And its distance from east to west is only 2933 km. l which of the following reasons is responsible for this?
a. The increasing distance between the two longitude lines towards the poles.
b. The decreasing distance between the two longitudinal lines towards the poles
c. Decreasing distance between two latitudinal line
d. Increasing distance between two latitudinal lines
Ans. (b)



